Prestressing in Detail - Post-tensioned tendons
Introduzione e presupposti
Innanzitutto, iniziamo con una breve descrizione del nostro software di progettazione del calcestruzzo. Questo articolo riguarda principalmente la progettazione del calcestruzzo precompresso nell'applicazione Detail, che è generalmente sviluppata per la progettazione di regioni di discontinuità o per la progettazione di elementi contenenti regioni di discontinuità, come aperture, estremità tagliate, ecc.
Per confrontare i risultati, utilizzeremo l'applicazione Beam il cui scopo, come si può intuire dal nome, è la progettazione di travi in calcestruzzo.
In secondo luogo, è necessario definire alcune ipotesi e restrizioni per comprendere meglio la progettazione di travi in cemento armato precompresso in dettaglio.
- L'analisi in funzione del tempo (TDA) non è implementata nell'applicazione Detail. Per contro, la TDA è implementata nell'applicazione Beam per la progettazione di travi in cemento armato precompresso.
- La TDA può essere simulata in Detail utilizzando il coefficiente di scorrimento e gli incrementi.
- I carichi di ritiro e di temperatura non sono implementati nel Dettaglio.
- Il calcestruzzo in tensione nel Dettaglio è escluso. Quindi, per il nostro confronto, dobbiamo avere una trave senza fessure. Naturalmente, lo stesso approccio può essere utilizzato in generale per le travi affette da fessure, ma i risultati non saranno gli stessi nella Trave perché in essa è previsto solo il calcolo lineare.
Incrementi
Prima di passare all'esempio, è necessario capire come funzionano gli incrementi per la progettazione del calcestruzzo precompresso nel Dettaglio.
Ci sono 3 tipi di carico che vengono applicati al modello in tre incrementi nell'applicazione Detail.
- precompressione - per l'incremento P
- Permanente - per l'incremento G
- Variabile - per l'incremento V
Se si crea una combinazione contenente casi di carico di tutti i tipi di carico, l'intera porzione del tipo di carico Precompressione sarà applicata al primo incremento P, l'intera porzione del tipo di carico Permanenti sarà applicata al secondo incremento G e l'intera porzione del tipo di carico Variable sarà applicata al terzo incremento V.
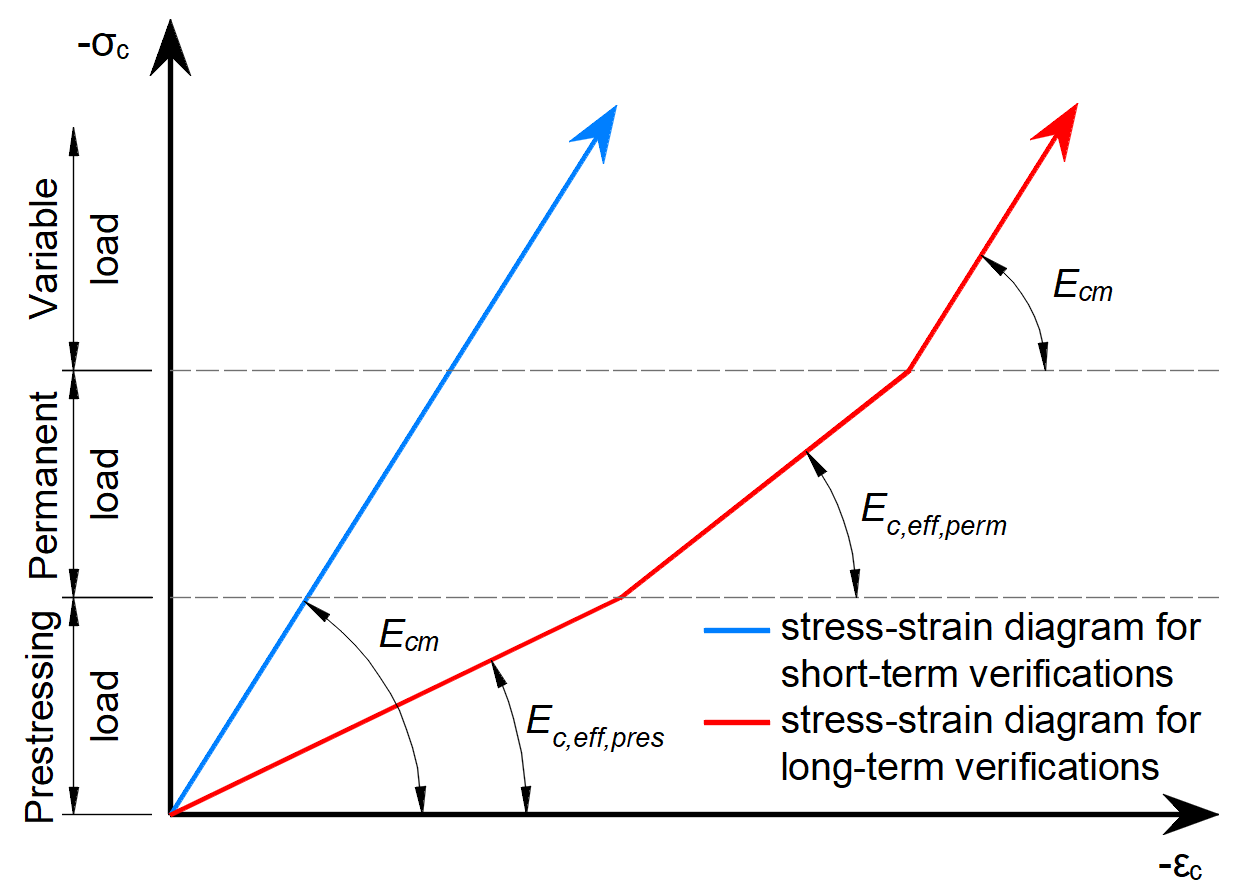
Il motivo per cui ci sono incrementi è che per i calcoli SLE vengono utilizzati diversi modelli di materiale (diversi moduli di elasticità), per SLU c'è un solo modello di materiale definito in Material model (EN).
Come si può vedere, ci sono tre moduli di elasticità:
- Ec,eff,press =Ecm / (1+φpress) - Modulo di elasticità effettivo del calcestruzzo per l'incremento di P
- Ec,eff,perm =Ecm / (1+φperm) - Modulo di elasticità effettivo del calcestruzzo per l'incremento G
- Ecm - Modulo di elasticità secante del calcestruzzo
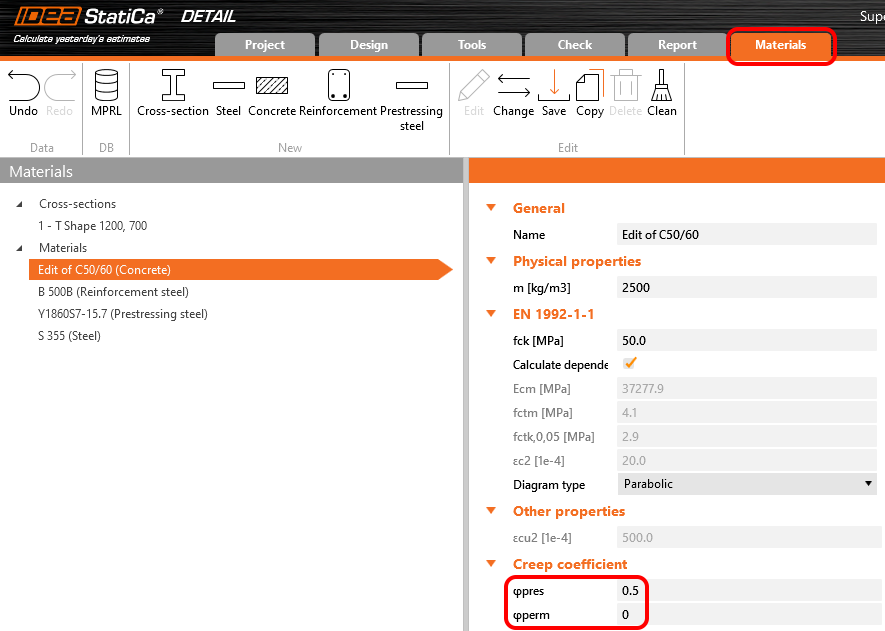
Dove φpress e φperm sono i coefficienti di scorrimento per gli incrementi P e G. I coefficienti possono essere impostati in Materiali e modelli.
Si noti che per gli effetti a breve termine si utilizza solo Ecm . È valido per tutti e tre gli incrementi. La perdita a lungo termine viene presa in considerazione solo per gli effetti a lungo termine.
The beam parameters
Two identical models are created in the Beam and Detail applications. They are attached at the end of this article. Download them and go through them while reading the article.
The example of a concrete beam will be introduced in the Beam application and then the comparison with the Detail application will be done for three construction stages.
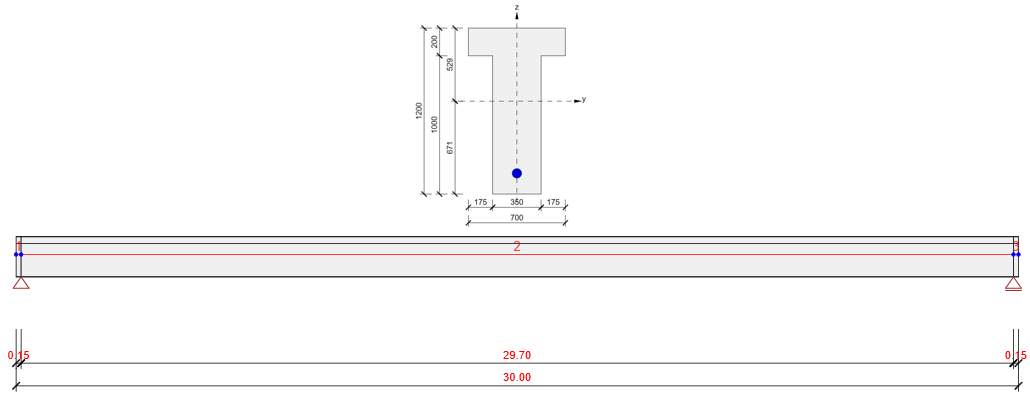
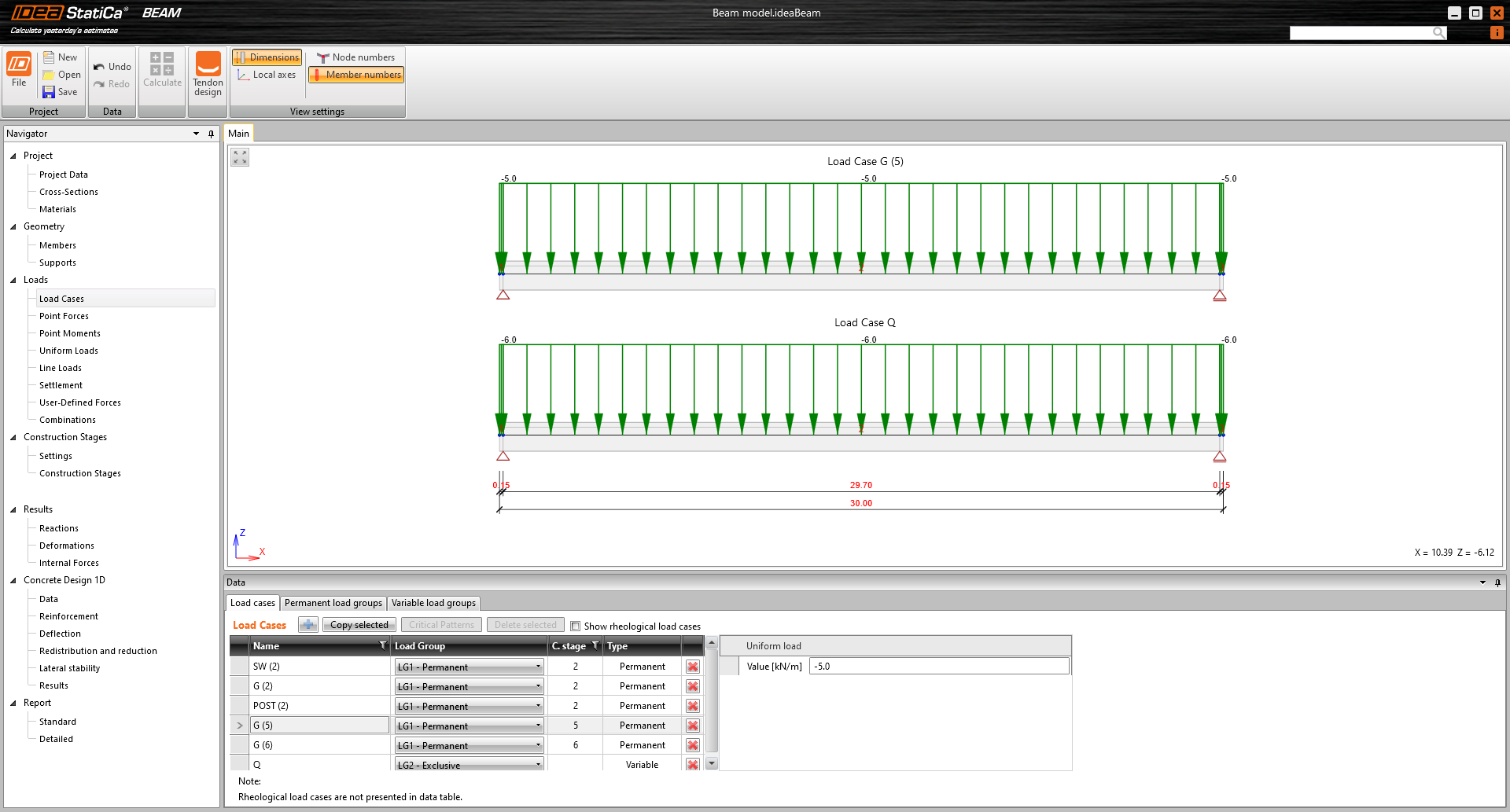
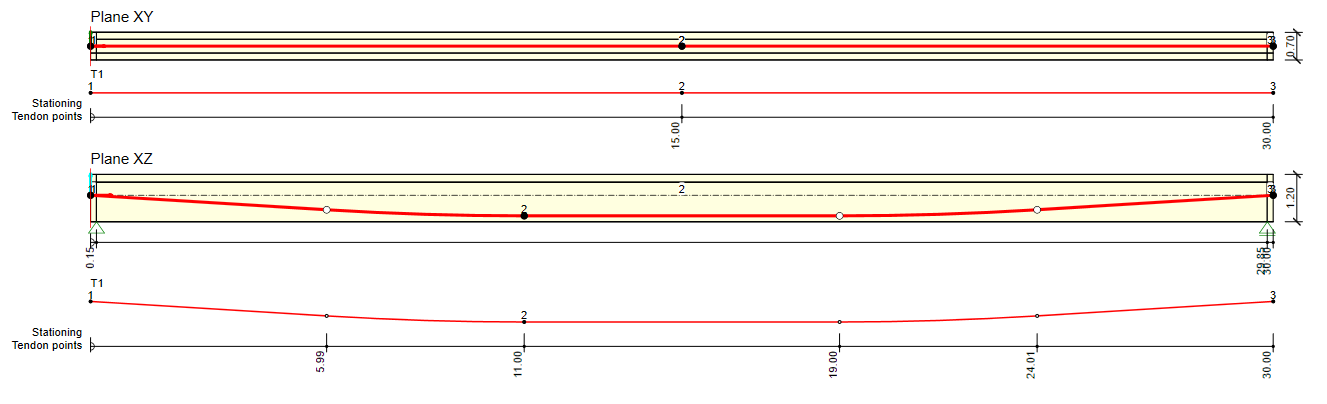
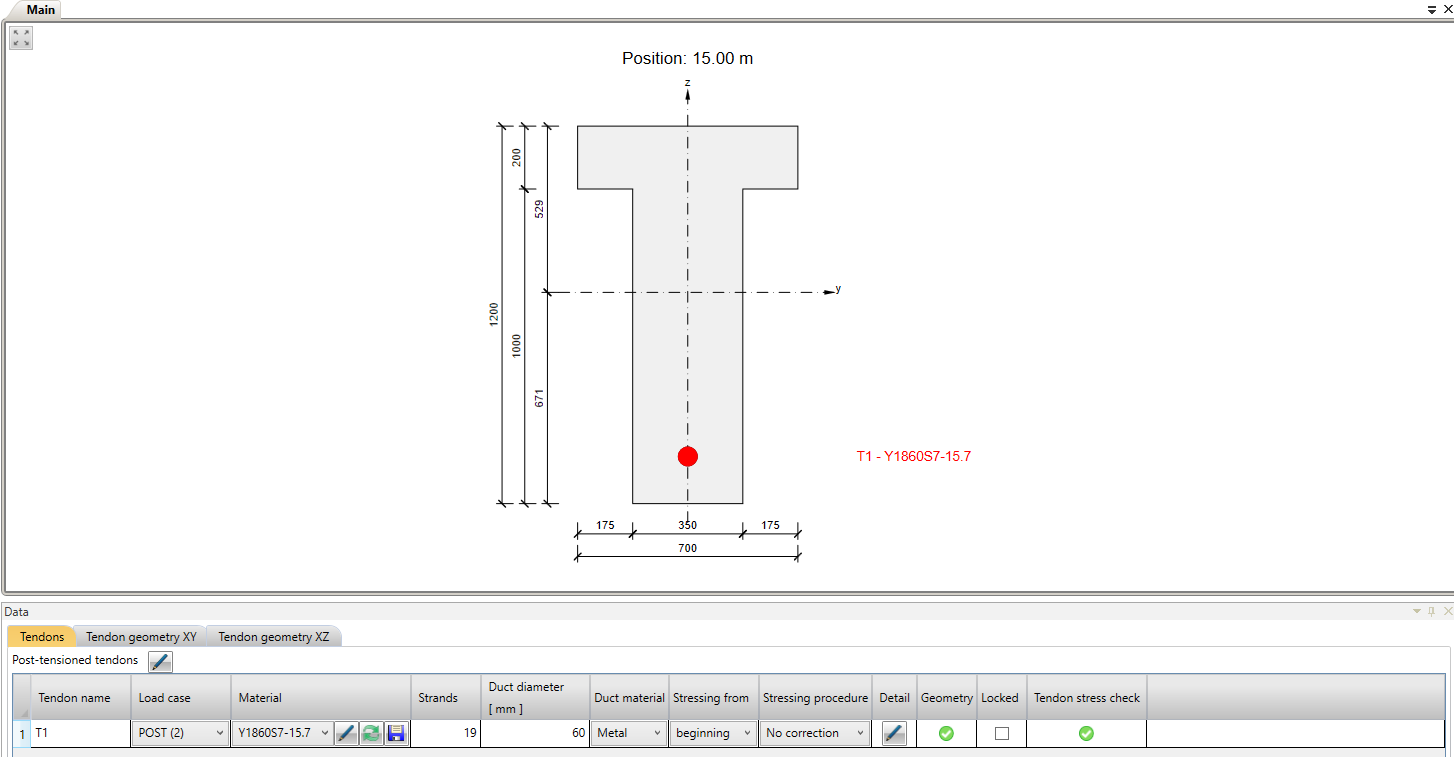
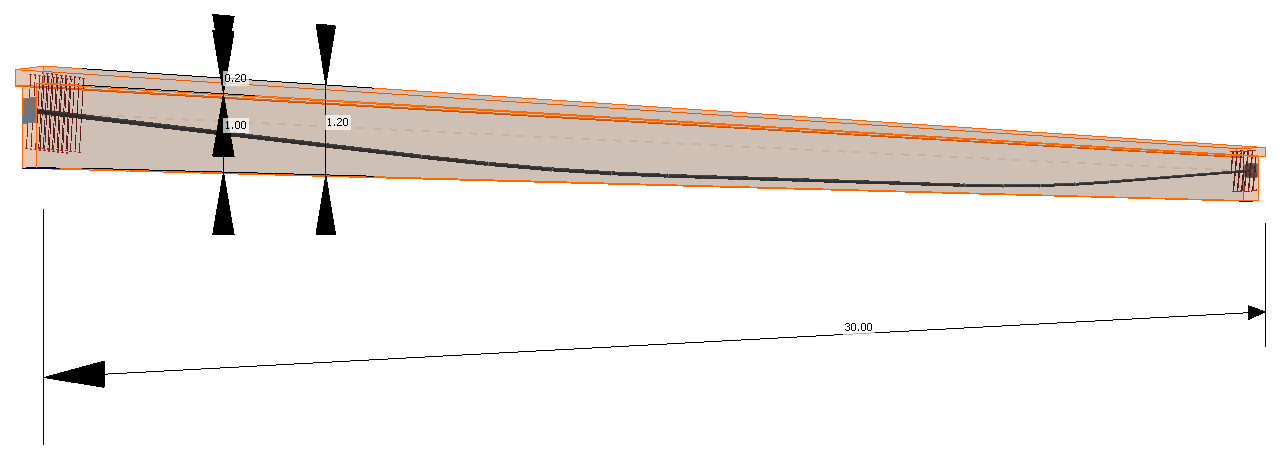
The example is a single span simple beam of T cross-section made of C50/60 concrete prestressed by a post-tensioned 19-strand tendon.
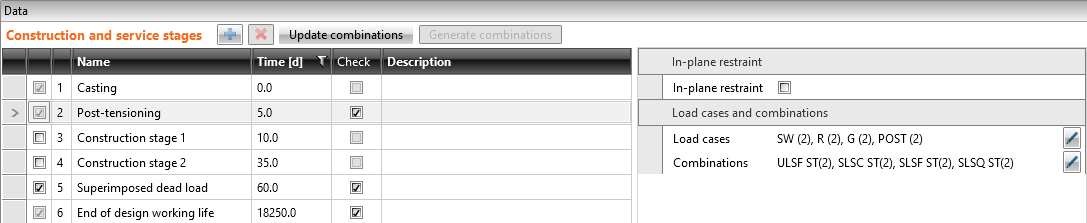
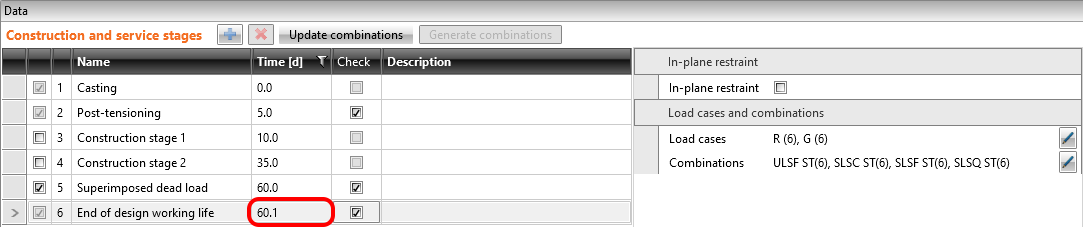
We will check the beam in three construction stages.
- Transfer of prestressing - 5 d (just after application of prestressing)
- Superimposed dead load - 60 d (start of working life)
- End of design working life - 18250 d (50 years)
The other stages can be carried out similarly.
There are only four load cases input. The numbers in the brackets are the numbers of the construction stages where the individual loads are applied.
- Self-weight - SW (2)
- Prestressing - POST (2)
- Permanent load - G (5)
- Variable load - Q
Other load cases are empty.
Now let's take a look at the prestressing. There is one 19-strand tendon. Note the diameter of the duct. The Beam application takes into account the weakened cross-section by the duct. On the other hand, the Detail application takes into account the full section. So to get the best possible match of results the duct diameter was set with the smallest possible diameter in the Beam application.
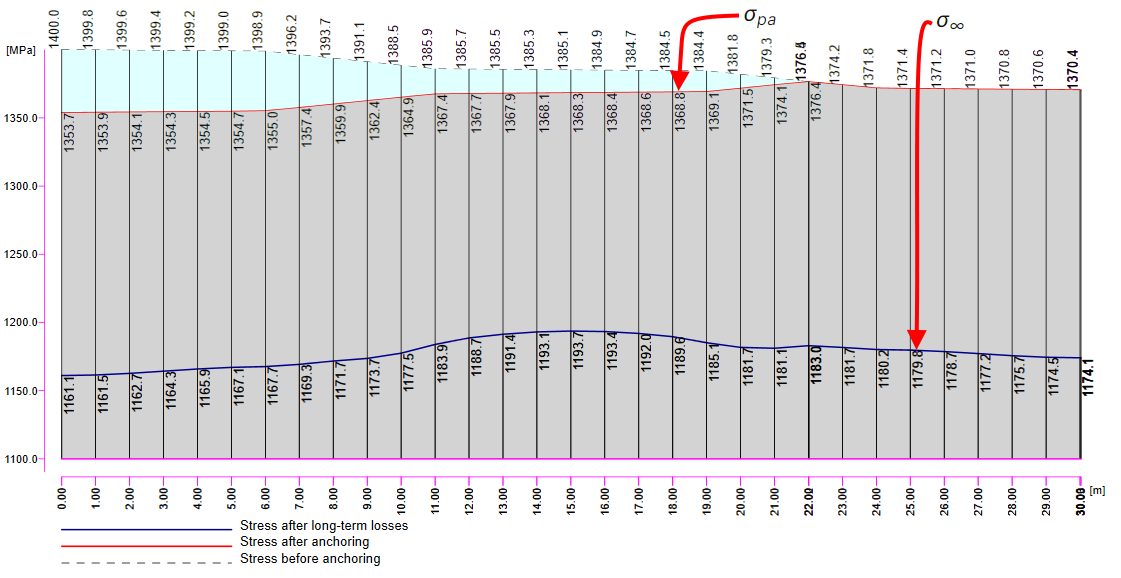
In the next figure, you can see the Tendon Stress/Losses chart.
There are several values of stress in the tendon that should be controlled during the prestressing application. At this point, we will stop and briefly explain the prestressing process and individual stresses and losses.
Prestressing process for post-tensioned beam
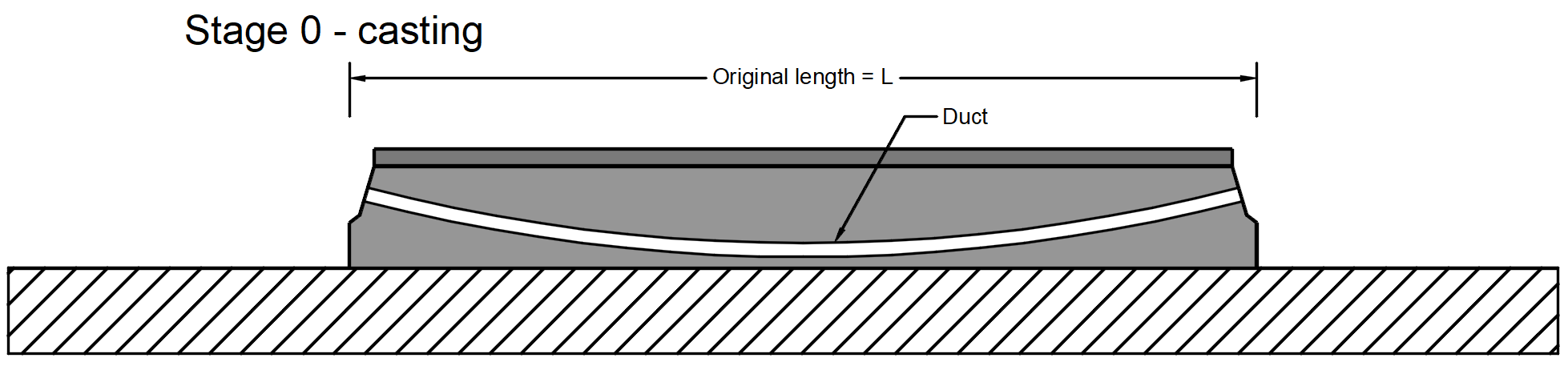
Stage 0 - casting -> The concrete member is cast containing reinforcement and an empty duct.
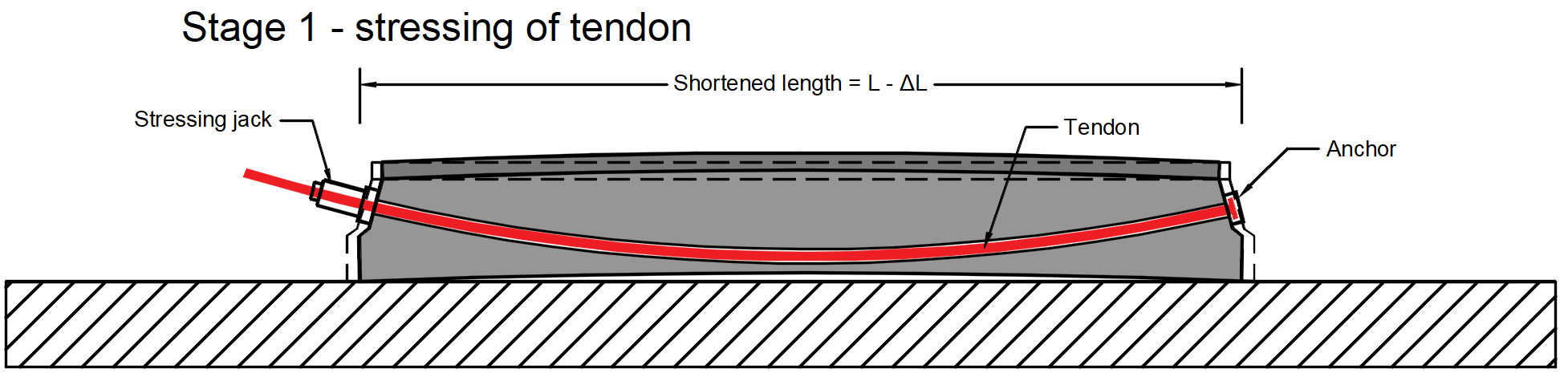
Stage 1 - stressing of tendon -> The tendon is inserted into the duct, anchored on one side and prestressed by stressing jack on the other side (or it can be stressed in two steps from both sides, but it is not our case). During the stressing process, the beam deforms. So there is initial stress σp,ini at the stressing jack, stress before anchoring in the tendon which is an initial stress affected by the frictional loss Δσpμ. In our example σp,ini = 1400 MPa.
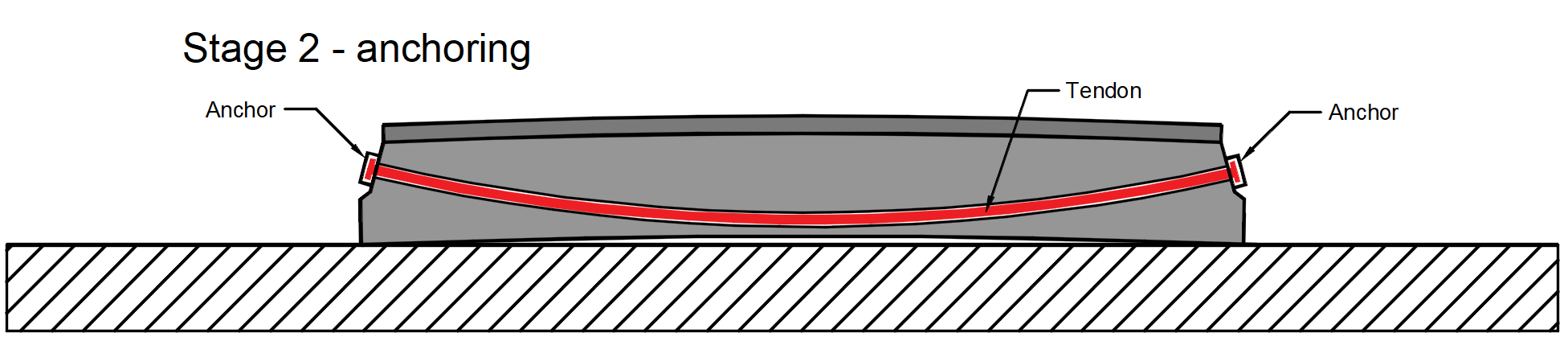
Stage 2 - anchoring -> The stressed end is anchored and the anchorage set loss (slip) Δσpw happens. There is no other loss due to the immediate elastic concrete strain because the immediate elastic concrete strain was realized before anchoring. The stress after anchoring (after short-term losses) σpa will be in the tendon at the end of this stage.
In the case of post-tensioned tendons, you can input the prestressing effect in Detail in two ways.
- Short-term losses are calculated automatically - The input is the Anchorage stress (initial stress) σp,ini. The losses Δσpμ and Δσpw are calculated automatically based on the Anchorage set, the Friction coefficient, and the Unintended angular change which are also inputs in this case.
- Short-term losses are defined by the user - The input is the stress after anchoring (after short-term losses) σpa. You input the value of the stress in each vertex of the tendon.
Note that in Detail the automatic calculation of short-term losses doesn't include the correction of relaxation. It was also turned off on the Beam in our example.
- Read more: Prestressing in Detail - Model description
Transfer of prestressing stage
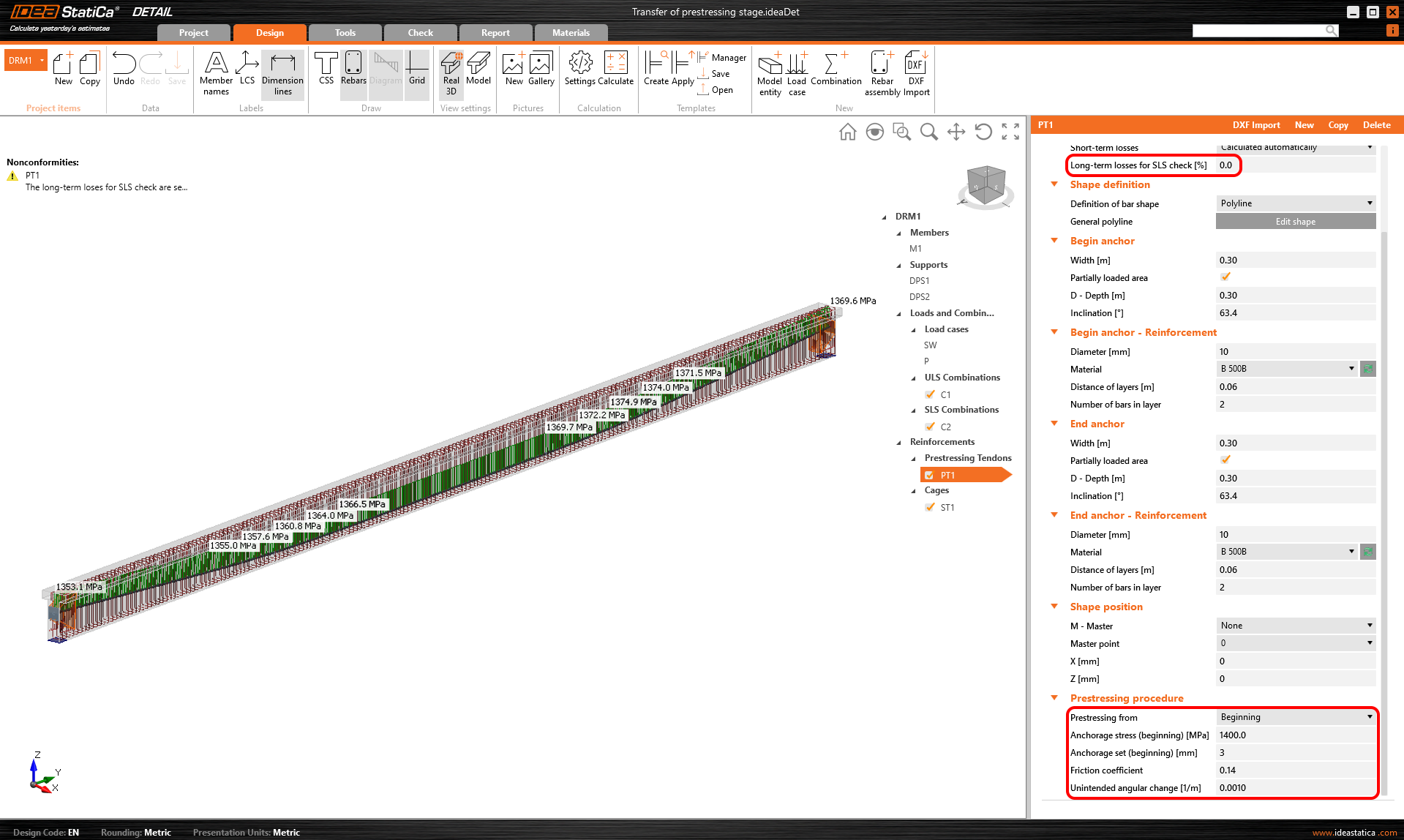
The model is defined so let's switch to the Detail application and have a look at how to set the first stage. The model is the same we only added stirrups for shear transfer, but it will not influence the results.
For this stage, there are only two load cases:
- SW - Prestressing type (Self-weight)
- P - Prestressing type (Prestessing)
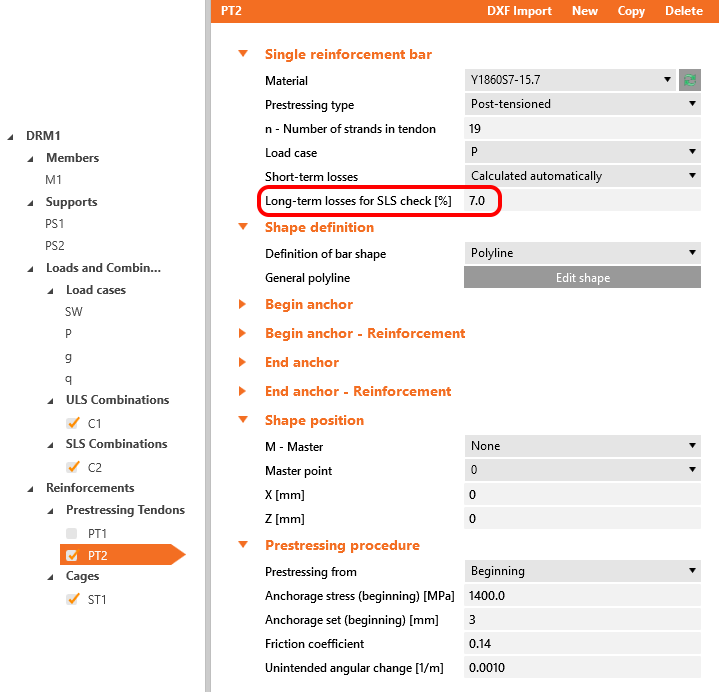
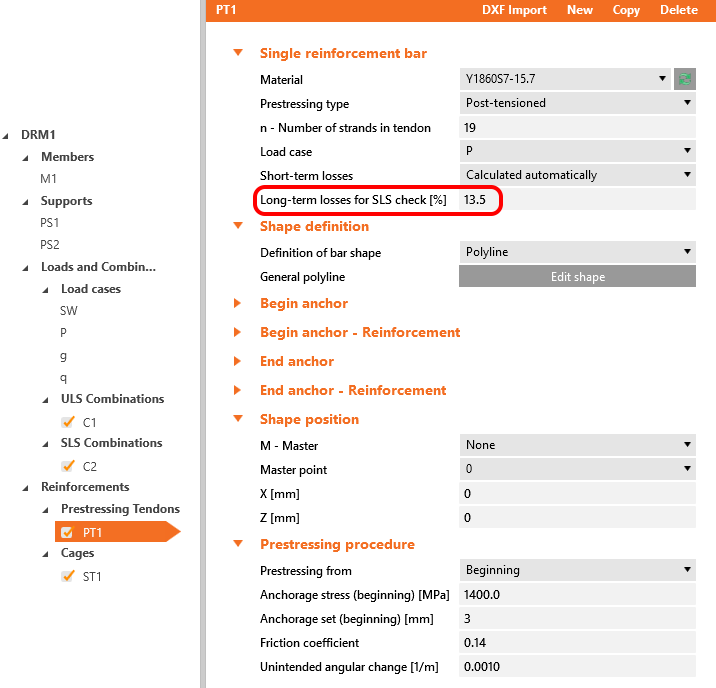
Both of them will be applied in the first load increment. Long-term losses for SLS checks are set to 0% and the values for the prestressing procedure are input the same as for the model in the Beam application. You can also compare automatically calculated stress after short-term losses σpa with the Tendon Stress/Losses chart from Beam.
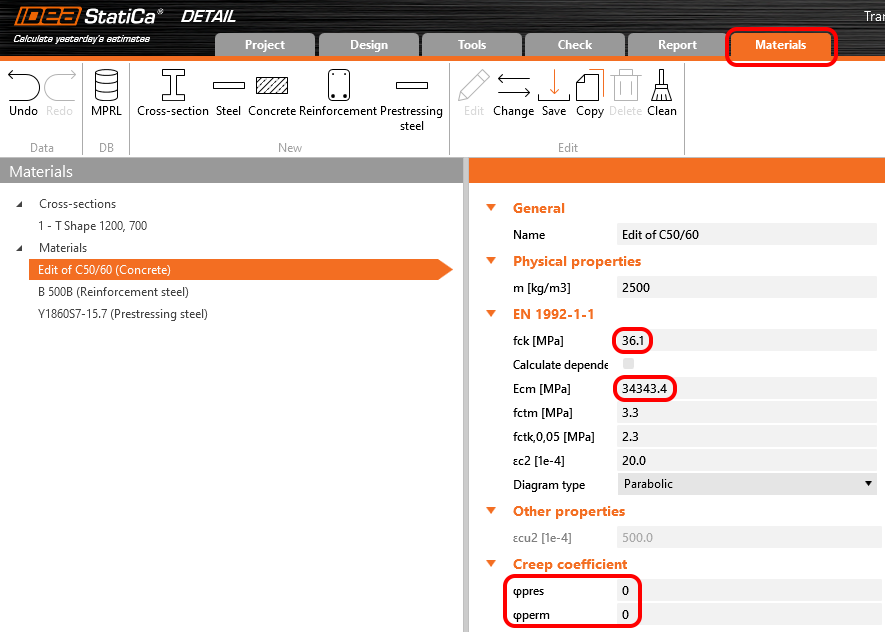
Creep coefficients are also set to zero value because we want to assess the stage just after the transfer of prestressing. And you can also notice that the value of Ecm and fck was rewritten to 5 days values we input into the Beam.
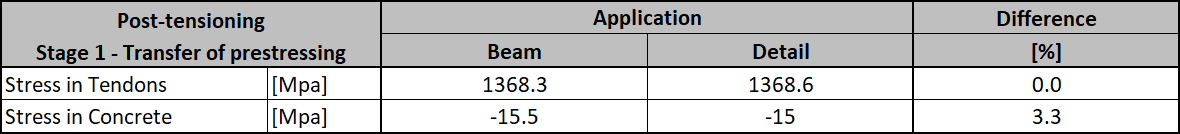
So let's compare the results. In that case, the long-term and short-term effects are the same. Because we didn't input any long-term loss.
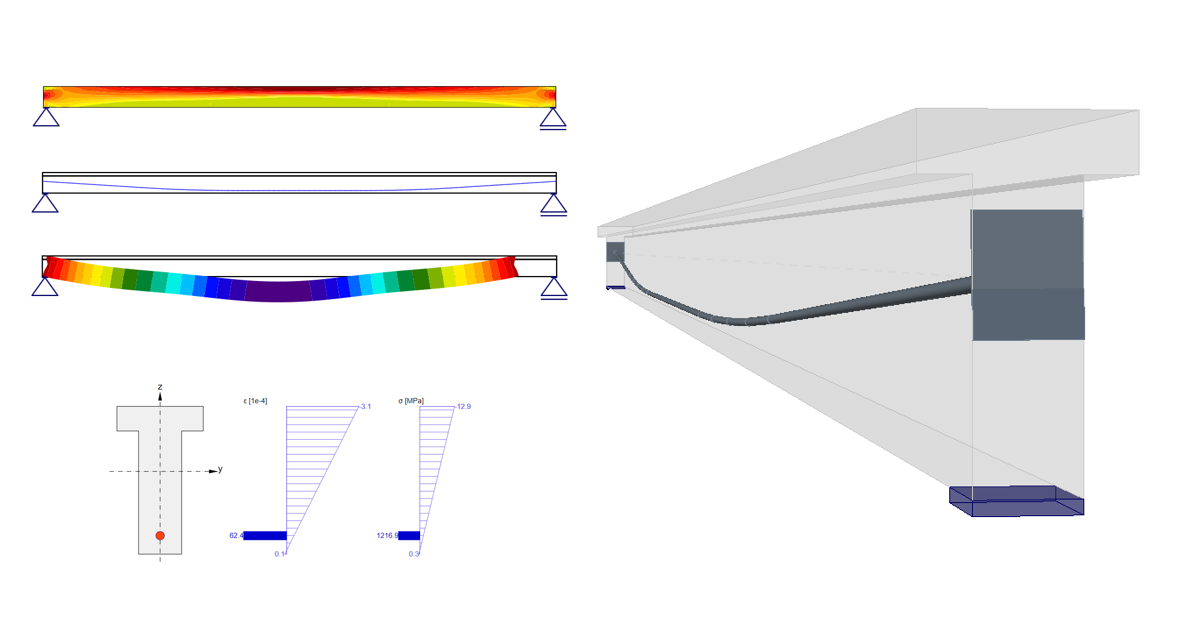
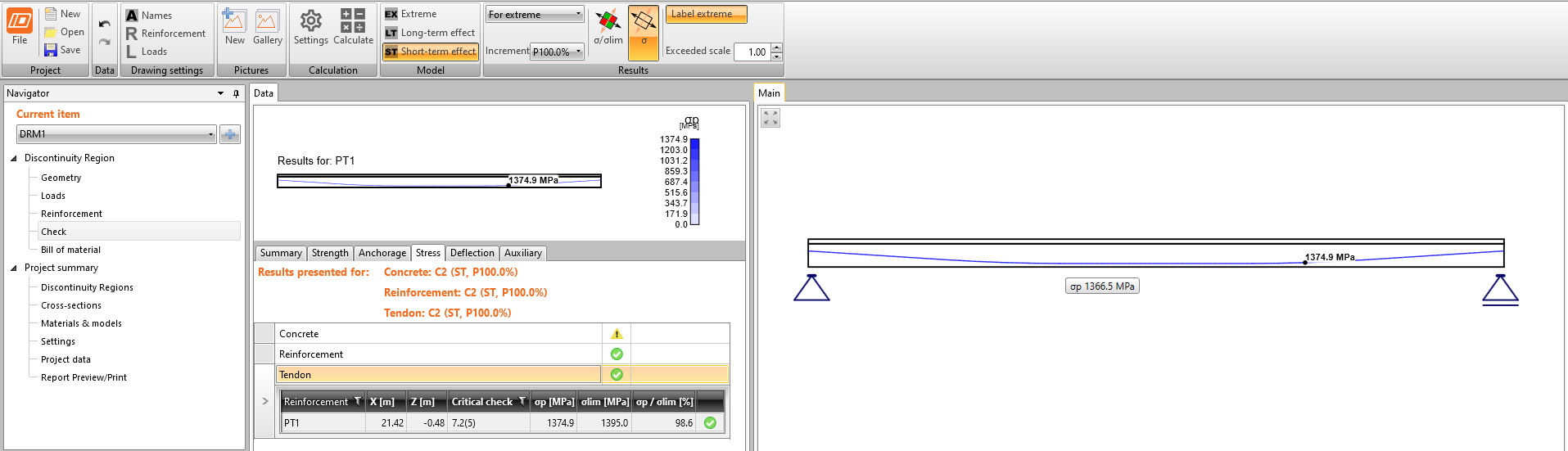
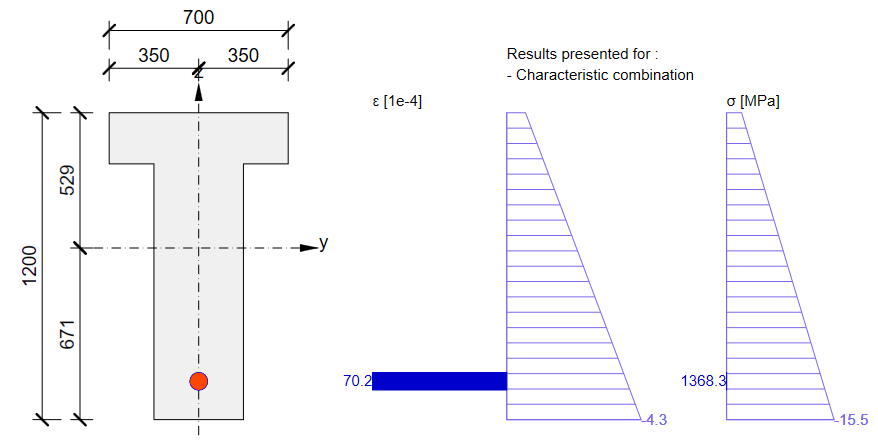
Stress in tendons in SLS - stress after short-term losses σpa:
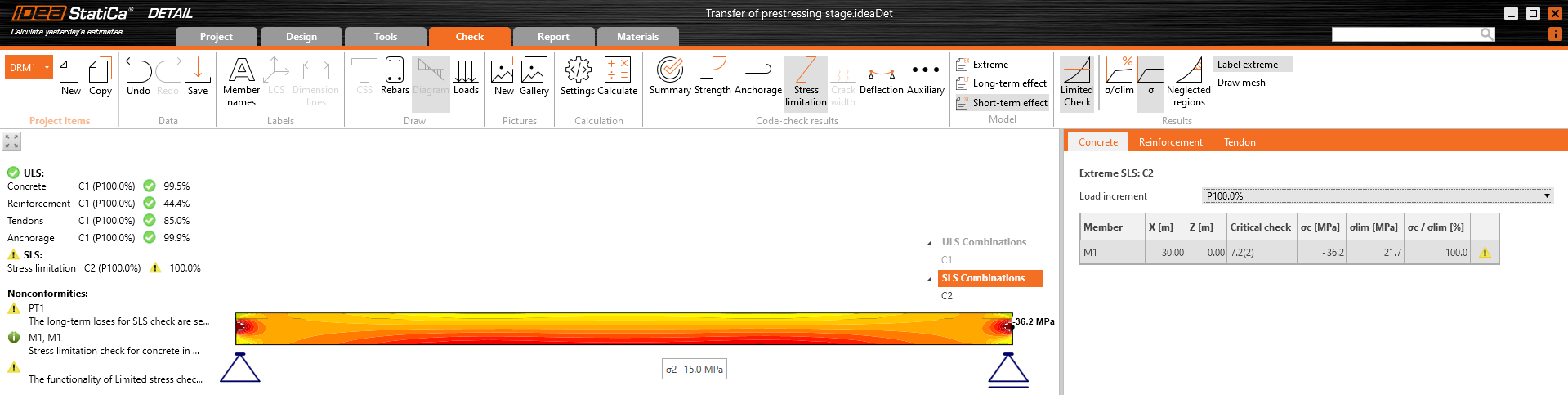
Stress in concrete in SLS:
The SLS section check from Beam:
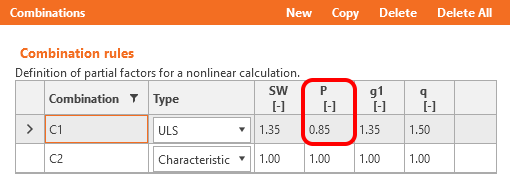
As you can see there is a good match. So it seems we have done the input for this stage correctly. Note that the coefficients rinf and rsup defined in EN 1992-1-1; 5.10.9 (1) was set as 1.0 in Beam.
For ULS there will be greater difference. This is because of a different approach used in the Beam application to determine the response in ULS. In this case, the additional increment you can see in Beam results are unbalanced stresses. This is a completely different complex topic. The important thing is that the bearing capacity would be almost the same in the Detail and Beam applications.
Now you know how to use the Detail app for the design of prestressed concrete structures using post-tensioned tendons for the Transfer of prestressing stage. Just change the geometry and add some discontinuities like openings, etc.
Superimposed dead load stage
The time (age of the concrete) for this stage is 60 days. The purpose of this stage is to check the concrete beam at the start of its working life including permanent and variable loads. So the other two load cases are added. Load impulses are of course the same as in the Beam application model.
We need to determine two values as input for Detail.
- Creep coefficient for the time from 2 days to 60 days
- Estimation of long-term losses for the time from 2 days to 60 days
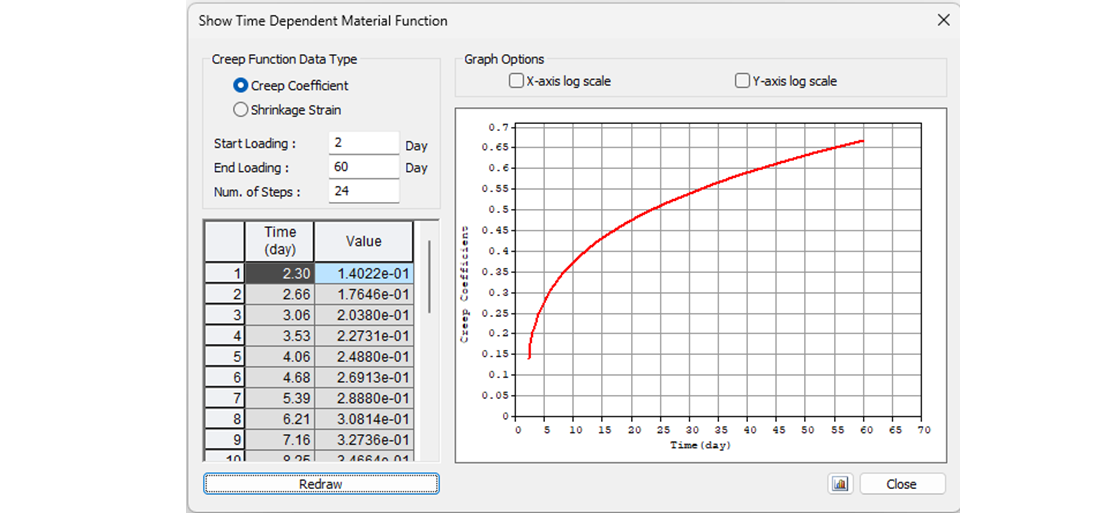
Let's start with the creep coefficient. In the following figure, you can see the creep function from 2 to 60 days for concrete grade C50/60 and cement class R according to the Eurocode. The value of the creep coefficient is then φpres ≈ φ(60) - φ(2) = 0.65 - 0.15 = 0.50
In Detail application, the creep coefficient can be set in Materials & models. It is obvious that the modulus of elasticity has to be set as the default Ecm value (recall the Increment chapter and the chart in it). You can also notice that the value of φperm = 0.0, which is because we want to apply permanent loads as short-time loads as well as variable loads.
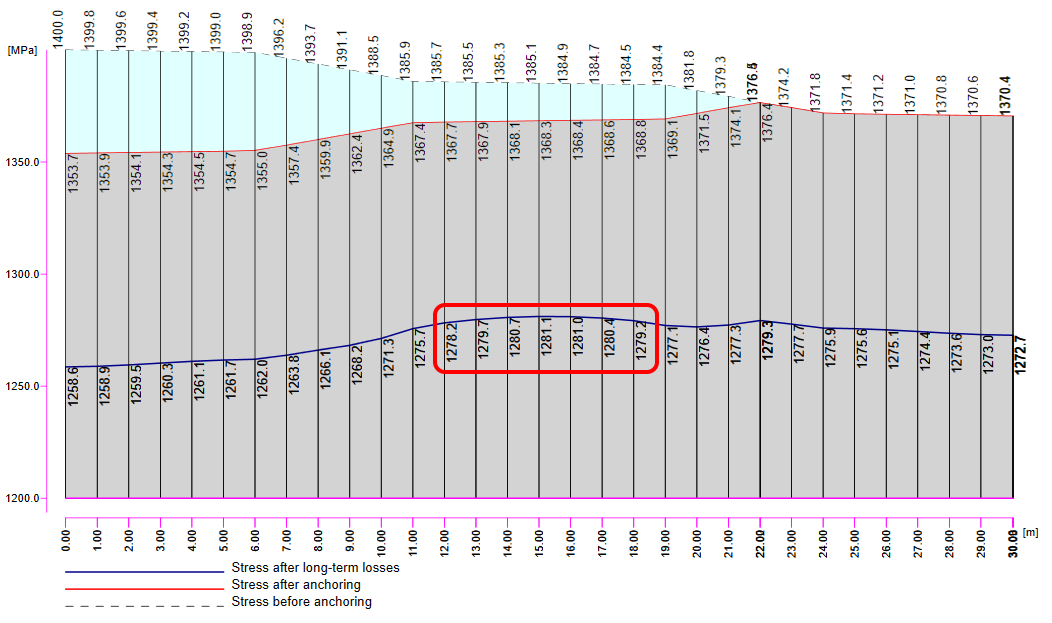
Now it is time for the long-term losses. Of course, you can estimate them (my estimation would be 8%). It is the easiest way, but in our example, we want to do it precisely. So we calculated σ60 - Stress after long-term losses in 60 days (blue line) in the Beam application by setting the final time to 60 days.
The value of σ60 = 1280 MPa as can be seen in the following figure (blue line).
Then we need to look at the value of σpa again. We have already confirmed that the values are the same in Beam and Detail.
In the figure, we can see that σpa = 1368.6 MPa in the middle of the span.
The long-term losses can then be calculated as σ60 / σpa = 1280 / 1368.6= 0.93 -> long-term loss is 7%. Let's input the value and compare the results.
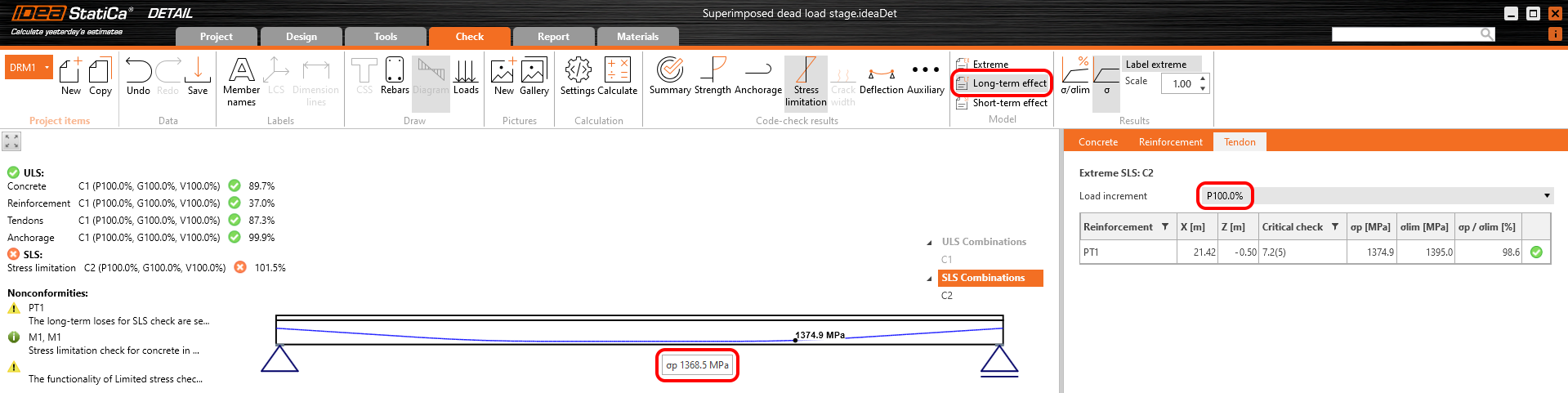
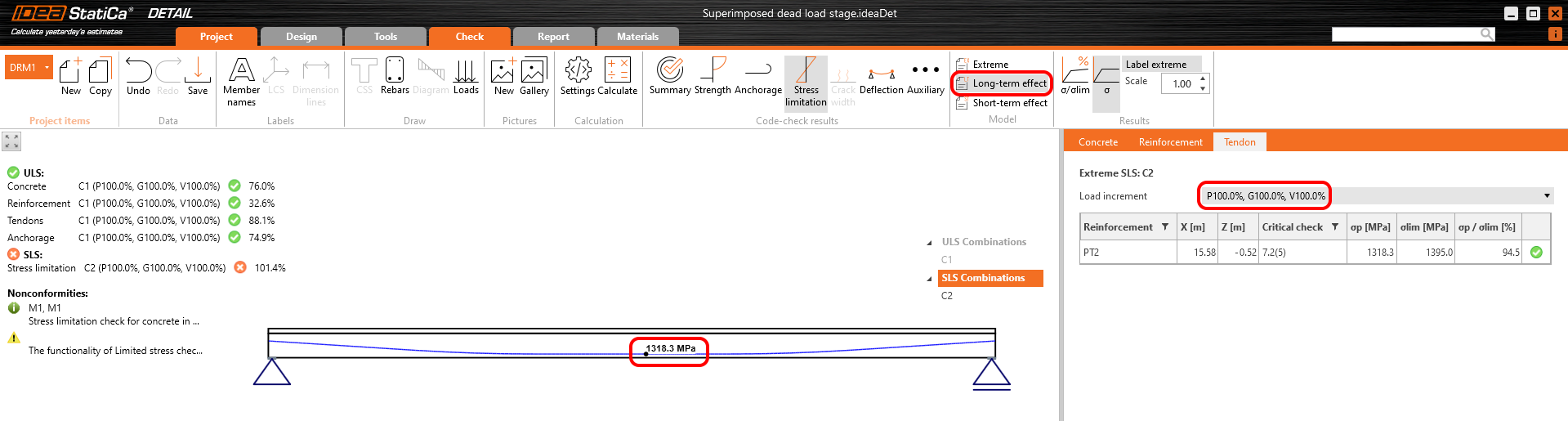
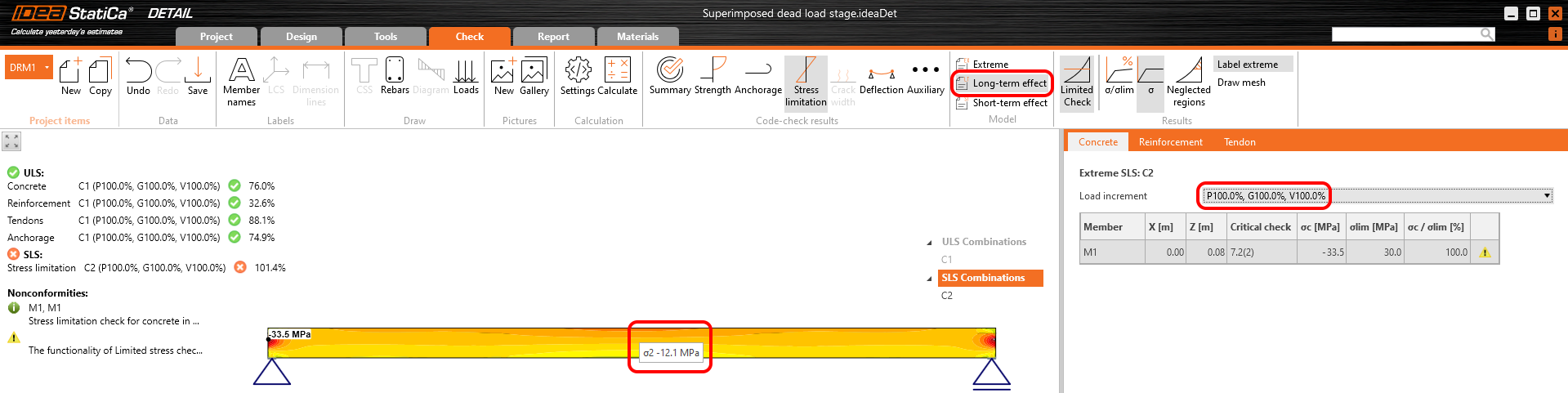
The results are read for long-term losses (we want to have creep and losses included) and for all increments (we want to have all loads included).
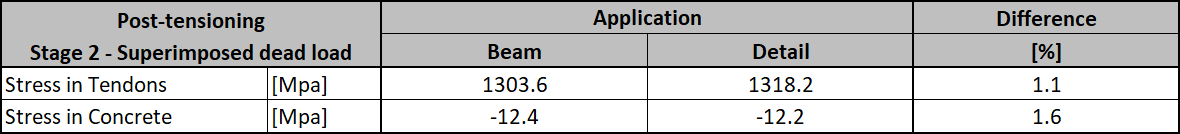
Stress in tendons in SLS:
Stress in concrete in SLS:
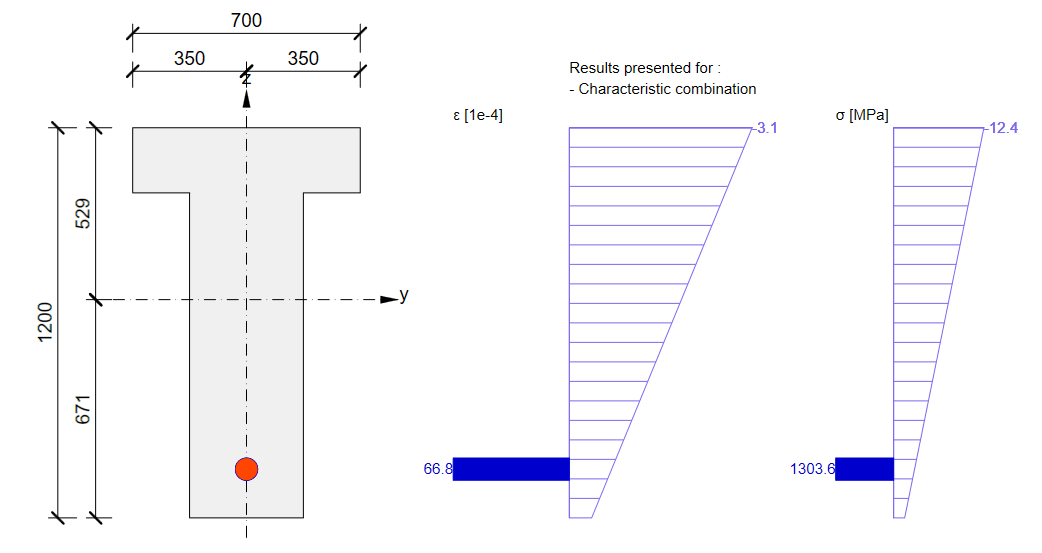
The SLS section check from Beam:
Again, there is a good match. So, it seems we have done the input for this stage correctly. For ULS there will be the same issue described in the previous stage. Note that the coefficients rinf and rsup defined in EN 1992-1-1; 5.10.9 (1) was set as 1.0 in the Beam application.
Now recall the beginning of this article where the increments were described. In the Detail application model for this stage, you can go through the individual increments to see the influence of individual load cases. You can also check the short-term effects which will differ from the previous Detail application model for the Transfer of prestressing stage. The reason is the different modulus of elasticity Ecm used in these models.
What you can actually see in the model for the Superimposed dead load stage in short-term effects is a Transfer of prestressing stage where t=28 days. So, if you don't need to prestress the beam before 28 days you don't need to create a special model for the design of prestressed concrete beams in the Transfer of prestressing stage.
End of design working life
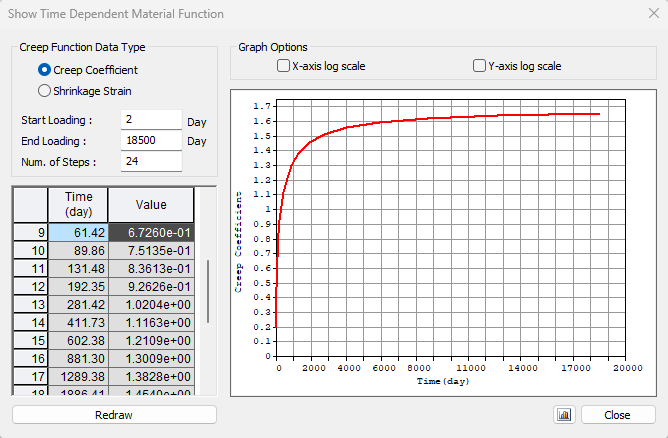
The approach will be the same as for the previous stage. First, we need to determine creep coefficients. In the following figure, you can see the creep coefficient function.
The value φpres ≈ 1.65 for the time from 2 to 18250 days for cement class R according to the Eurocode. The value φperm = φ(18250) - φ(60) ≈ 1.65 - 0.65 = 1.00 for the time from 60 to 18250 days. Note the highlighted value φ(60) in the table above.
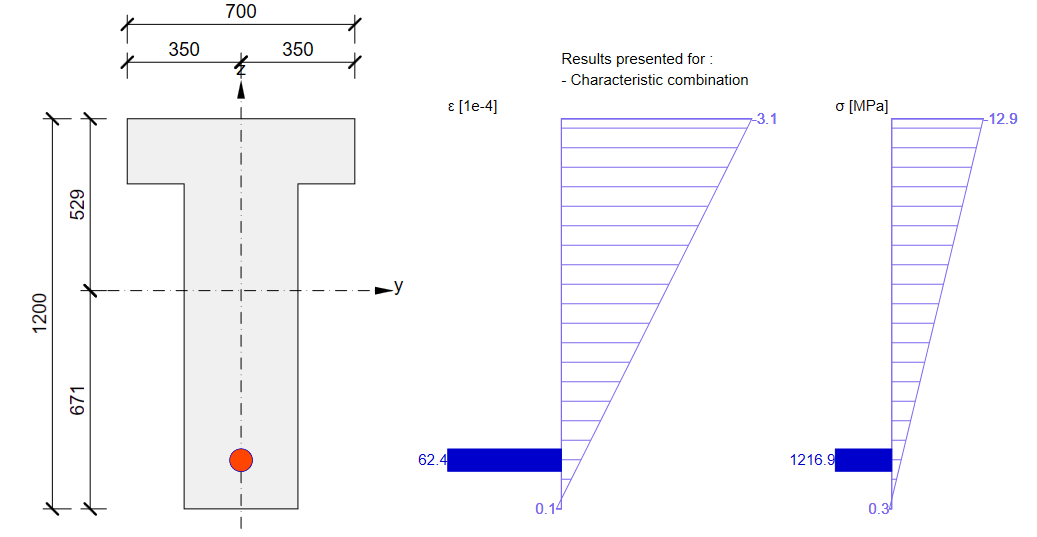
Then we need to look at the value of σpa again. We have already confirmed that the values are the same in Beam and Detail.
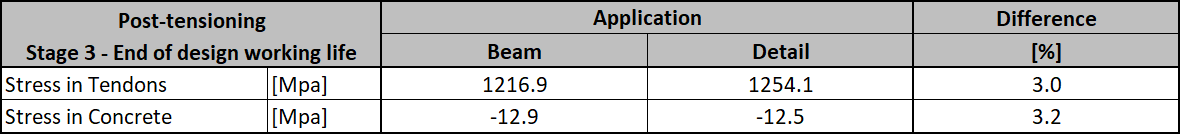
The long-term losses can be calculated as σ∞ / σpa = 1185 / 1368.6 = 0.865 -> long-term loss is 13.5%. The value of σ∞ is determined in The beam parameters chapter in the Tendon Stress/Losses chart. Let's input the value and compare the results.
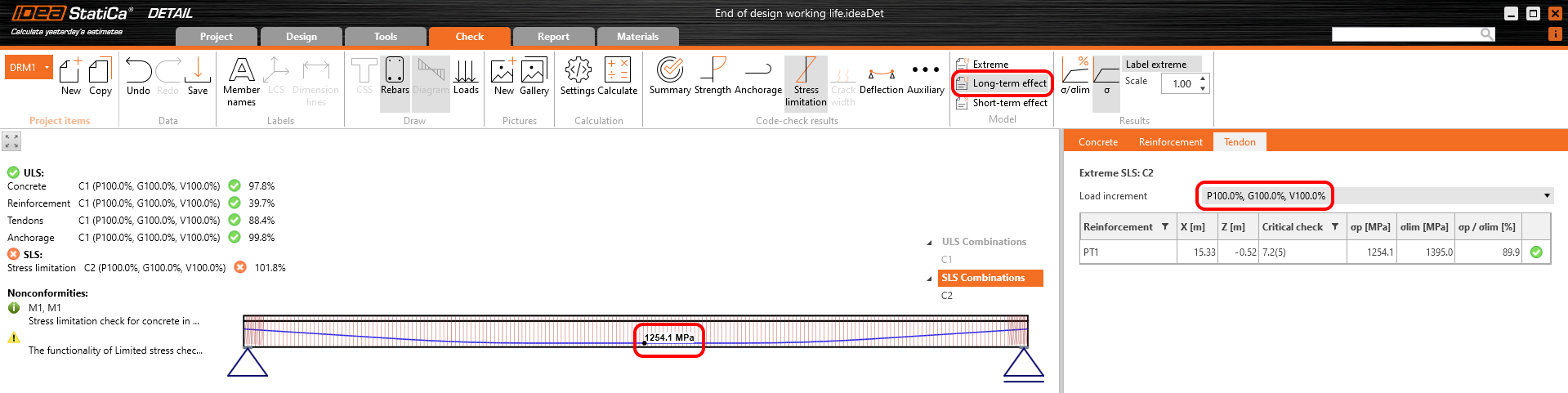
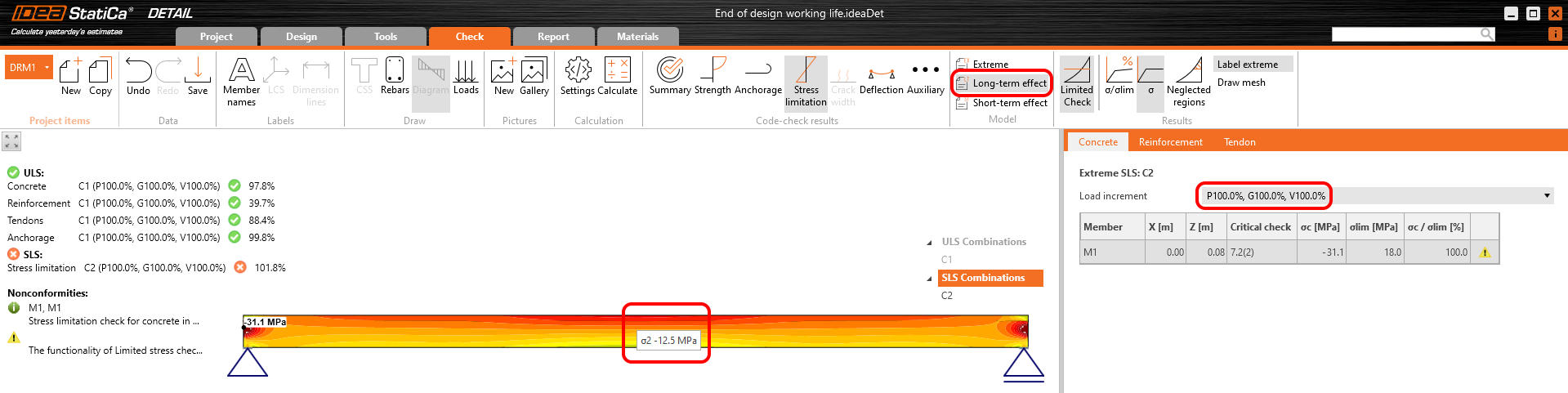
Stress in tendons in SLS:
Stress in concrete in SLS:
The SLS section check from Beam:
Conclusion
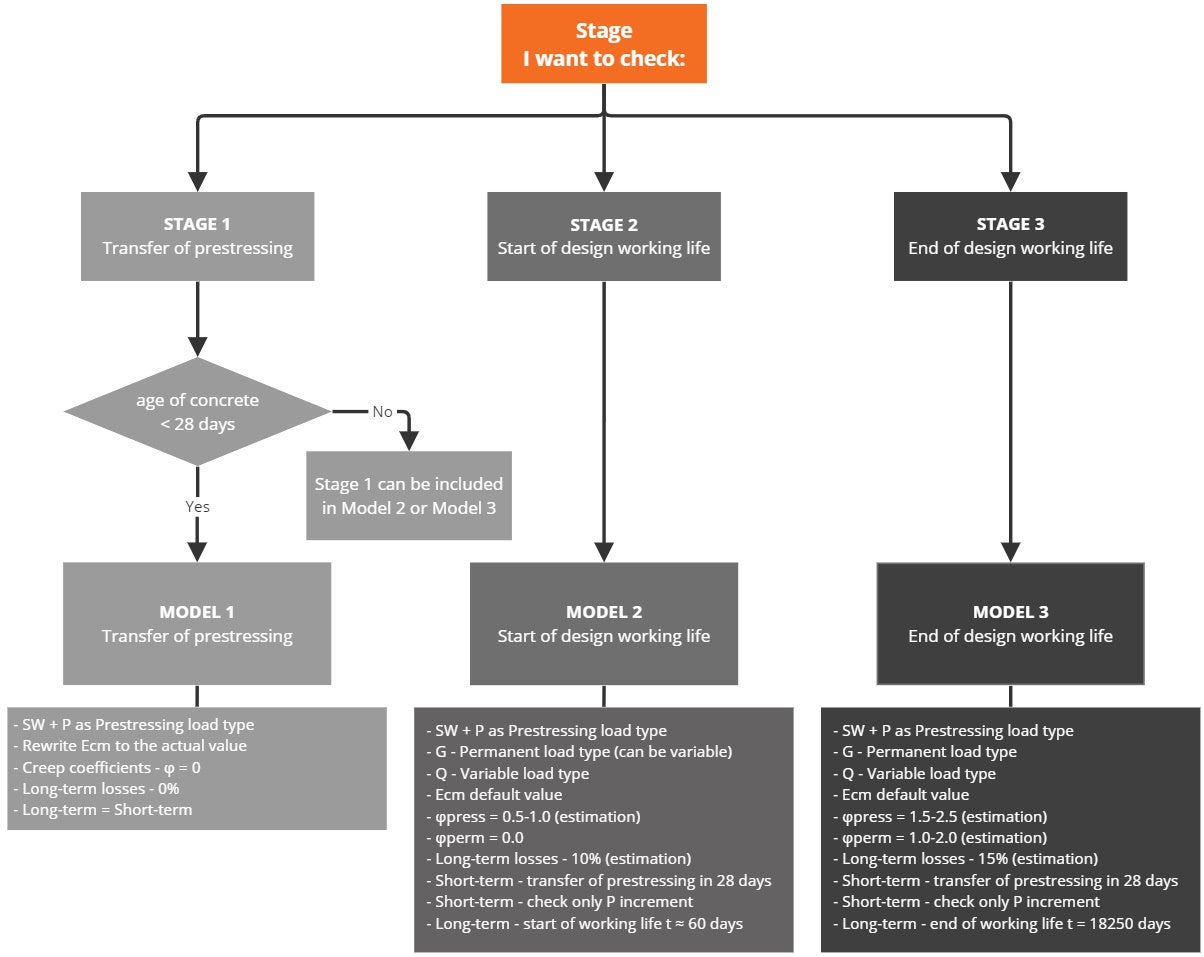
Finally, here is a simple workflow, where you can find the above-described procedure of designing the prestressed concrete structures in IDEA StatiCa Detail using post-tensioned tendons.
It's worth repeating that for post-tensioned tendons the anchorage stress or stress after short-term losses (user-defined type) has to be input. An estimation of the long-term losses due to creep, shrinkage, and relaxation should be input.
Note that in the attached Detail application models for Stage 2 and Stage 3 checks for short-term V increments are unsatisfactory. It follows from the preceding that for Model 2 and Model 3 for short-term effects, only the first increment P needs to be considered (since no other permanent loads, nor variable loads will be applied during applying prestressing). It is valid only if the age of concrete when applying prestressing is greater than 28 days, otherwise, you have to do a special model for Stage 1 (for short-term effects).
Long-term losses for ULS have to be set as a combination factor. The estimation of long-term losses which can be set in reinforcement is taken into account only for SLS checks. The input for the estimation of 15% should look like this:
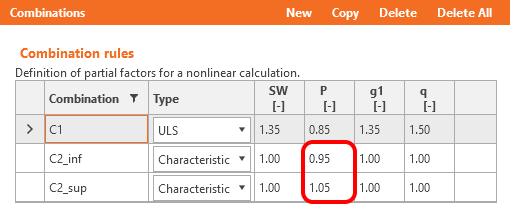
Coefficients rinf and rsup defined in EN 1992-1-1; 5.10.9 (1) for prestressing effects for SLS should be also taken into account in combinations. It means you should create at least two combinations. See the figure.
Read about the implementation of these coefficients in the Beam application in How the rinf and rsup coefficients are taken into account for SLS checks
You have read how to use IDEA StatiCa Detail a concrete design software where you can, among other things, do a design of prestressed concrete beams with discontinuities. But let's not forget about the IDEA StatiCa Beam, which is used for concrete beam design including TDA, and which we used for comparing the results.
Download allegati
- Superimposed dead load stage.ideaDet (IDEADET, 15 kB)
- End of design working life.ideaDet (IDEADET, 15 kB)
- Beam model.ideaBeam (IDEABEAM, 848 kB)
- Transfer of prestressing stage.ideaDet (IDEADET, 15 kB)